Understanding Esophageal Strictures
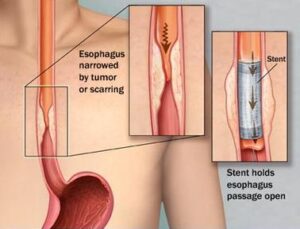
Esophageal strictures are narrowing’s of the esophagus, the tube that carries food and liquids from your mouth to your stomach. These narrowing’s can make swallowing difficult and painful, affecting your ability to eat and drink normally.
Imagine your esophagus as a garden hose. Normally, water flows through it easily. But if the hose gets pinched or blocked, the water flow slows down or stops. Similarly, when your esophagus narrows due to a stricture, food and liquids can’t pass through as smoothly.
What Causes Esophageal Strictures?
Several factors can lead to the development of esophageal strictures. Chronic acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common cause, where stomach acid repeatedly irritates the esophagus lining, leading to scar tissue formation. Other causes include:
-Injuries from medical procedures: Such as radiation therapy or surgical interventions. These can damage the esophageal lining and lead to scarring.
-Swallowing corrosive substances: Accidentally ingesting strong cleaning agents or other corrosive materials can cause severe burns and subsequent narrowing of the esophagus.
-Chronic inflammation: Conditions like eosinophilic esophagitis, which involves an allergic reaction causing inflammation, can lead to scarring over time.
-Infections: Certain infections, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems, can cause damage and scarring of the esophagus.
Symptoms of Esophageal Strictures
Recognizing the symptoms of esophageal strictures is crucial for timely treatment. Common symptoms include:
-Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia): You may feel like food is getting stuck or taking longer to move down.
-Painful swallowing (odynophagia): Swallowing may cause a burning or stabbing pain.
-Regurgitation of food: Food may come back up into your mouth after swallowing.
-Frequent heartburn or acid reflux: A burning sensation in your chest or throat.
-Unintentional weight loss: Difficulty eating can lead to nutritional deficiencies and weight loss.
-Persistent feeling of something stuck in the throat: This can be uncomfortable and distressing.
Diagnosis of Esophageal Strictures
Diagnosing an esophageal stricture typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests. These tests can include:
-Endoscopy: A flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the esophagus to view the stricture directly. This allows the doctor to see the extent and location of the narrowing.
-Barium swallow: A special X-ray that tracks the movement of a swallowed liquid to highlight narrow areas. You drink a barium solution, which coats the esophagus and makes it visible on X-rays.
-Esophageal manometry: Measures the rhythmic muscle contractions of the esophagus when swallowing. This test helps determine if the muscles in your esophagus are working properly.
Introduction to Esophageal Stricture Dilation
Esophageal stricture dilation is a medical procedure designed to stretch and widen the narrowed part of the esophagus, allowing food and liquids to pass more easily. This procedure is typically performed by a gastroenterologist using specialized tools.
The procedure usually involves sedating the patient to ensure comfort. During an endoscopy, the doctor will insert a dilator—a device that can be a balloon or a series of graduated dilators—into the esophagus. The balloon is inflated, or the dilators are progressively inserted to gently stretch the narrowed area.
Step-by-Step Process
- Preparation: The patient fasts for several hours before the procedure to ensure an empty stomach, which reduces the risk of aspiration (inhaling food or liquids into the lungs).
- Sedation: A sedative or anesthetic is administered to make the patient comfortable and prevent pain.
- Endoscopy: The doctor examines the esophagus using an endoscope to locate the stricture.
- Dilation: The dilator is inserted through the endoscope and gradually expands the stricture. If a balloon dilator is used, it is inflated to stretch the narrowing.
- Recovery: The patient is monitored in a recovery area until the effects of sedation wear off. This observation period ensures that there are no immediate complications.
Benefits of Esophageal Stricture Dilation
This procedure offers several significant benefits:
-Improved Swallowing: Patients often experience immediate relief in swallowing difficulties. This improvement can dramatically enhance their ability to eat and drink normally.
-Enhanced Nutrition: Easier swallowing means better nutritional intake. Patients can enjoy a wider variety of foods without fear of choking or pain.
-Quick Recovery: The procedure is minimally invasive with a relatively short recovery time. Most patients can return to their normal activities within a day or two.
-Symptom Relief: Reduces pain and discomfort associated with esophageal strictures, leading to a better overall quality of life.
Risks and Considerations
While esophageal stricture dilation is generally safe, it does come with potential risks:
-Bleeding: Minor bleeding can occur at the site of the dilation but is usually not serious and resolves on its own.
-Perforation: During the procedure, doctors rarely puncture the esophagus, which may require additional treatment and even surgery.
-Infection: There’s a small risk of infection, which can be managed with antibiotics if it occurs.
-Recurrent Strictures: Some patients may require repeated dilations if the stricture returns. Regular follow-ups with your doctor can help manage this risk.
Recovery and Aftercare
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
After the procedure, medical staff typically observe patients for a few hours until they are fully awake. Patients commonly experience mild throat discomfort, and medical staff recommend initially eating soft foods or liquids to avoid irritating the esophagus.
Long-Term Care
-Dietary Adjustments: Gradual reintroduction of solid foods as the esophagus heals. Start with soft foods and avoid very hot or cold foods, which can irritate the esophagus.
-Medication: Continued use of medications for underlying conditions like GERD to prevent recurrence of strictures. These medications can help manage acid reflux and reduce inflammation.
-Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups to monitor the esophagus and prevent recurrence. Your doctor may perform follow-up endoscopies to ensure the esophagus remains open.
Comparing Esophageal and Urethral Stricture Dilation
Both esophageal and urethral stricture dilations involve similar principles of using dilators to widen narrow passages. The different parts of the body are addressed by separate specialists during the procedures. Urethral stricture dilation targets the urethra to improve urinary flow, often due to scar tissue from infections, surgeries, or trauma.
Key Differences
–Location: The esophagus undergoes esophageal dilation, while the urethra undergoes urethral dilation.
-Symptoms: Esophageal strictures primarily cause swallowing difficulties, while urethral strictures cause urinary issues such as difficulty urinating and urinary retention.
-Specialists: Gastroenterologists perform esophageal dilations, while urologists perform urethral dilations.
When to Consider Esophageal Stricture Dilation?
You should consider this procedure if:
-You experience persistent difficulty swallowing that interferes with your daily life.
-Medications and lifestyle changes have not improved your symptoms.
-Diagnostic tests confirm a significant esophageal stricture.
-Swallowing issues severely impact your quality of life, leading to nutritional deficiencies and weight loss.
Conclusion
Esophageal stricture dilation can be a life-changing procedure for those suffering from swallowing difficulties due to esophageal strictures. By understanding the procedure, its benefits, and potential risks, you can decide whether this treatment is right for you. Always consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms and explore the best treatment options tailored to your needs.
