Understanding Foreign Bodies
– Foreign bodies encompass any object that enters the body through ingestion, inhalation, or penetration through the skin.
– They can vary widely in size, shape, and composition, ranging from tiny particles like dust or sand to larger objects like glass fragments, fish bones, or even jewelry.
– Depending on where they lodge themselves, foreign bodies can cause a range of symptoms and complications, from minor discomfort to severe injury or infection.
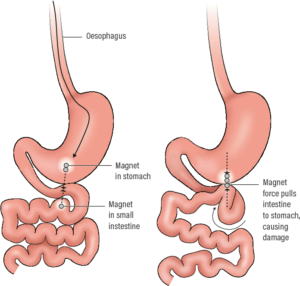
Common Types of Foreign Bodies
Foreign bodies can be classified into two main categories: external and internal.
– External Foreign Bodies: These are objects that penetrate the skin, such as splinters, thorns, nails, or fragments of glass or metal. They can cause pain, swelling, and sometimes lead to infection if not promptly removed.
– Internal Foreign Bodies: These objects are ingested or inhaled and can include food items (such as bones or small toys), coins, or even small tools. They may remain asymptomatic or cause symptoms such as choking, abdominal pain, or difficulty breathing.
Symptoms of Foreign Body Presence
– Symptoms of a foreign body presence can vary widely depending on the type, size, and location of the object.
– A person may experience localized pain, swelling, redness, discomfort, coughing, choking, difficulty breathing, or a sensation of something being stuck.
– In some cases, particularly with internal foreign bodies, symptoms may be subtle or absent initially, making it important to seek medical attention if there is any suspicion of ingestion, inhalation, or penetration.
Importance of Prompt Removal
– Prompt removal of foreign bodies is crucial to prevent complications such as infection, tissue damage, or obstruction of vital organs or airways.
– Even seemingly innocuous objects can cause significant harm if left untreated, as they may migrate deeper into tissues or lead to chronic inflammation and infection.
– Delaying treatment can also increase the risk of complications and may necessitate more invasive procedures for removal.
Foreign Body Removal Techniques
– Extraction Devices: Tweezers, forceps, or suction devices may be used to grasp and remove external foreign bodies.
– Endoscopic Techniques: For internal foreign bodies, endoscopy (a minimally invasive procedure using a flexible tube with a camera) may be employed to visualize and retrieve the object from within the body’s cavities or organs.
– Surgical Intervention: In cases where objects are deeply embedded or pose a significant risk, surgical intervention may be necessary to safely remove the foreign body.
Preparation for Removal Procedure
-During the examination and medical history review before the removal procedure, the nature, location, and potential complications associated with the foreign body will be assessed.
-The doctor may order imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasound to precisely locate and evaluate the extent of a foreign body.
– Based on the findings, we may need to take additional preparatory steps such as fasting, sedation, or antibiotic prophylaxis to optimize the safety and efficacy of the procedure.
What Happens During the Removal?
– The specific removal procedure will depend on factors such as the type, size, and location of the foreign body.
– Local anesthesia may be administered to numb the area and minimize discomfort during the procedure.
– For external foreign bodies, the object may be grasped with specialized instruments and gently pulled or manipulated out of the skin.
– Internal foreign bodies may be extracted safely using endoscopic techniques or surgical intervention.
Aftercare and Recovery
– The doctor will clean and dress the affected area, provide specific post-procedure instructions, and remove the foreign body once it has been taken out successfully.
– The doctor may recommend over-the-counter analgesics or prescription medications for pain management to alleviate discomfort.
-Follow-up appointments may be scheduled to monitor healing and resolve symptoms.
Risks and Complications
– While foreign body removal procedures are generally safe, there are inherent risks and potential complications associated with any invasive medical procedure.
– These may include infection, bleeding, damage to surrounding tissues or structures, allergic reactions to anesthesia or medications, or failure to completely remove the foreign body.
-Complications can vary based on factors like foreign body type, location, patient health, and provider expertise.
When to Seek Medical Help
-Seek medical attention promptly if you have a foreign body or symptoms.
– Avoid attempting to remove the object yourself, as this can lead to further injury, complications, or difficulty in subsequent medical management.
Conclusion
Foreign body removal by doctors is a vital aspect of healthcare that addresses the potentially serious consequences of objects entering the body where they shouldn’t be. From small splinters to ingested objects, foreign bodies can cause discomfort, pain, and even life-threatening complications if left untreated. Prompt recognition and removal of foreign bodies are essential to prevent complications and promote healing.
Seeking medical aid is crucial when suspecting a foreign body to avoid worsening injuries or complications.
By staying informed about the risks and procedures involved in foreign body removal, you can take proactive steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. Remember, timely intervention and proper medical care are key to ensuring a safe and successful outcome. If you suspect there’s a foreign object, don’t hesitate to go to a doctor.
